Homework requirements
Setup your personal Github page.
- Setup your environment to work with github (see below for specific instructions)
- Create a new repository on Github with the name
{your-handle}.github.io - Setup a local repository in your environment
- Setup the github repo as a remote in your local repository
- Create an index.html file with a “Hello world” greeting
- Commit and push the index file
- Make sure that the greeting is deployed to your github page at https://{your-handle}.github.io
- Every day for 5 days:
- make changes to the index file
- commit the changes
- push them to remote repository
Suggestions
The contents of the page is NOT important for the course. The important part is to practice using git daily - committing and pushing changes.
You can add multiple pages to your site and link them together - feel free to experiment and apply knowledge from other courses.
Add a readme file that describes how your code works.
Use the git status, and git log command to examine your repository state and history.
Practice staging only part of the changes you’ve made. Try to write meaningful commit messages.
Guide: Setup Github repository
- Log into your Github profile
 (starting with an empty github profile is not required)
(starting with an empty github profile is not required)
Before we create a our repository we will setup our authentication
- Open your Github settings
We will use create BOTH a PAT (personal access token) and an SSH key. This will allow you to push to the repositories through either HTTPS or SSH.
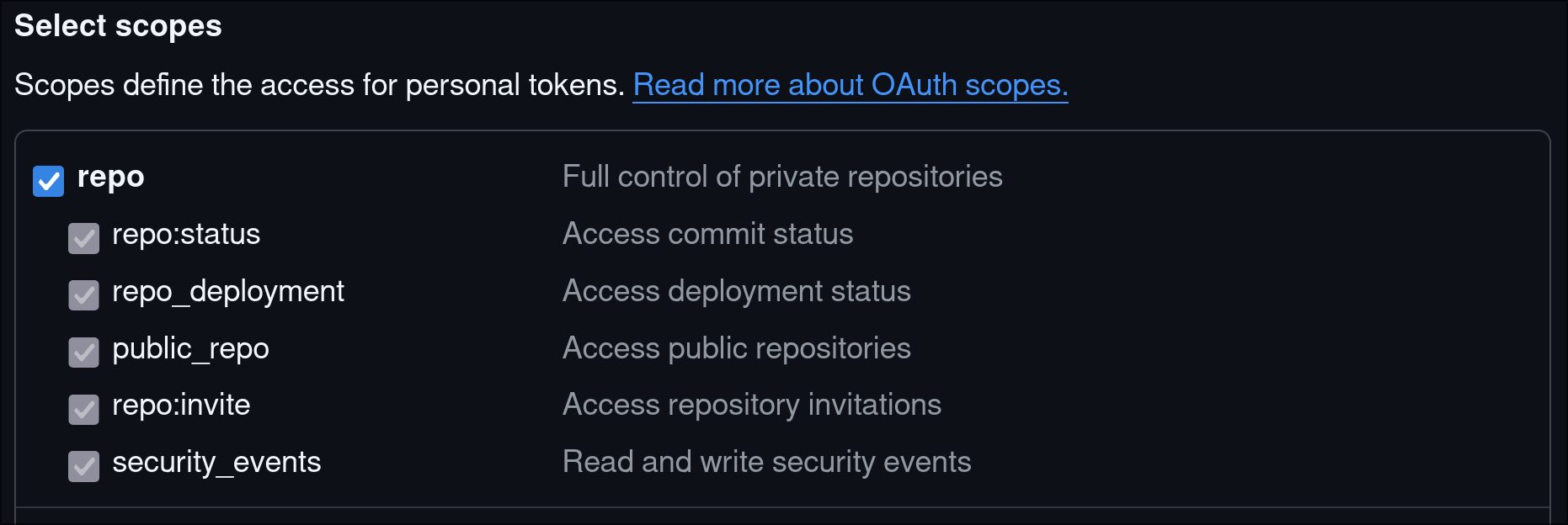
- Add an classic access token with all repository scopes
COPY and SAVE your token
- In your environment, create an ssh key pair
On MacOS and Linux (including online terminal): See details about using the online terminal below
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "{your-email}"On Windows with Git for Windows using the bash console.
More details how to install git with bash for windows will be listed below.
ssh-keygen.exe -t ed25519 -C "{your-email}"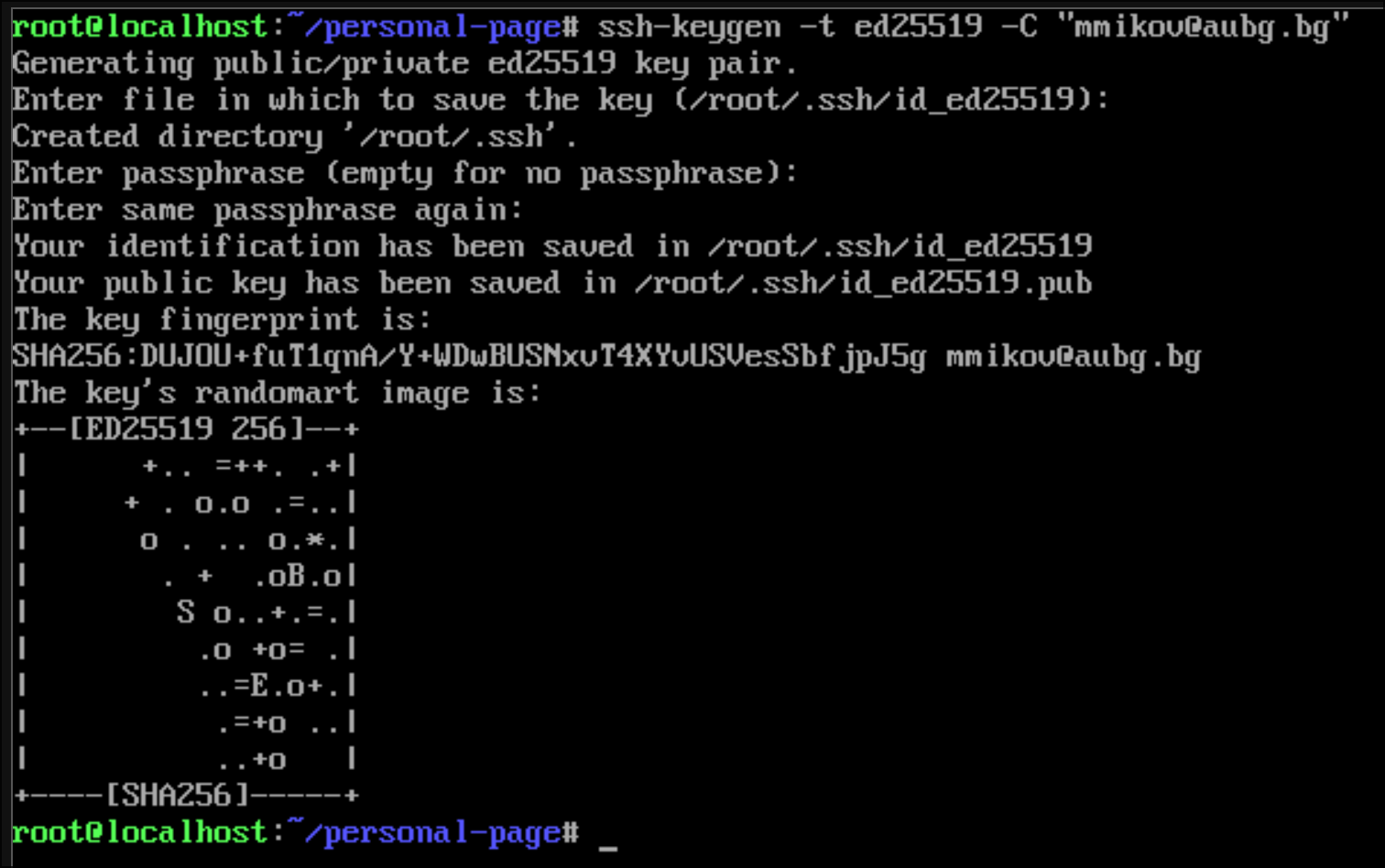
The above commands will create 2 files in the ~/.ssh/ directory:
id_ed25519- your private key - DO NOT SHARE THISid_ed25519.pub- your public key - copy this to Github
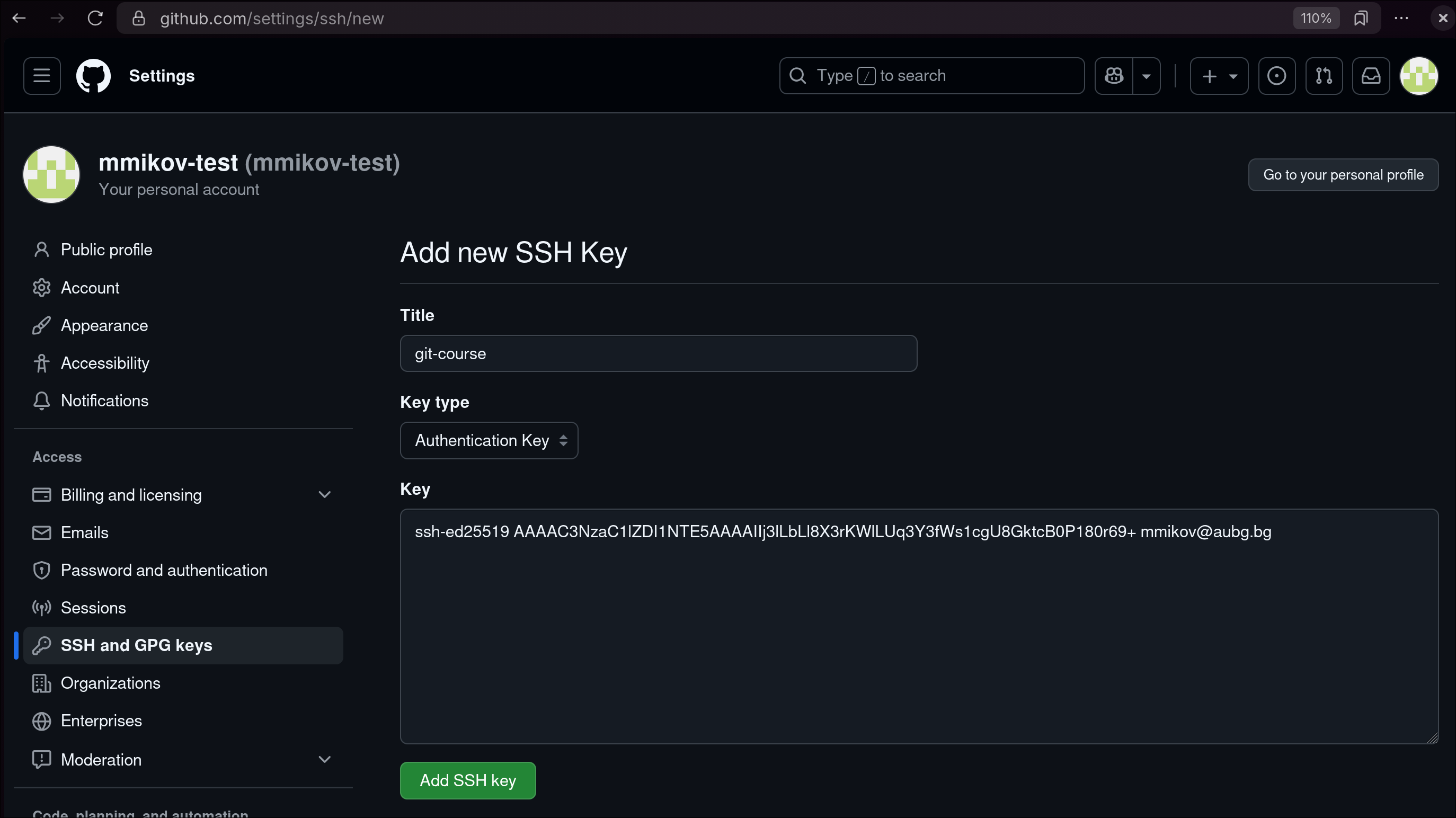
- Add the public key to Github
Open the SSH keys tab in your Github settings

Paste the full contents of the id_ed25519.pub file and save it
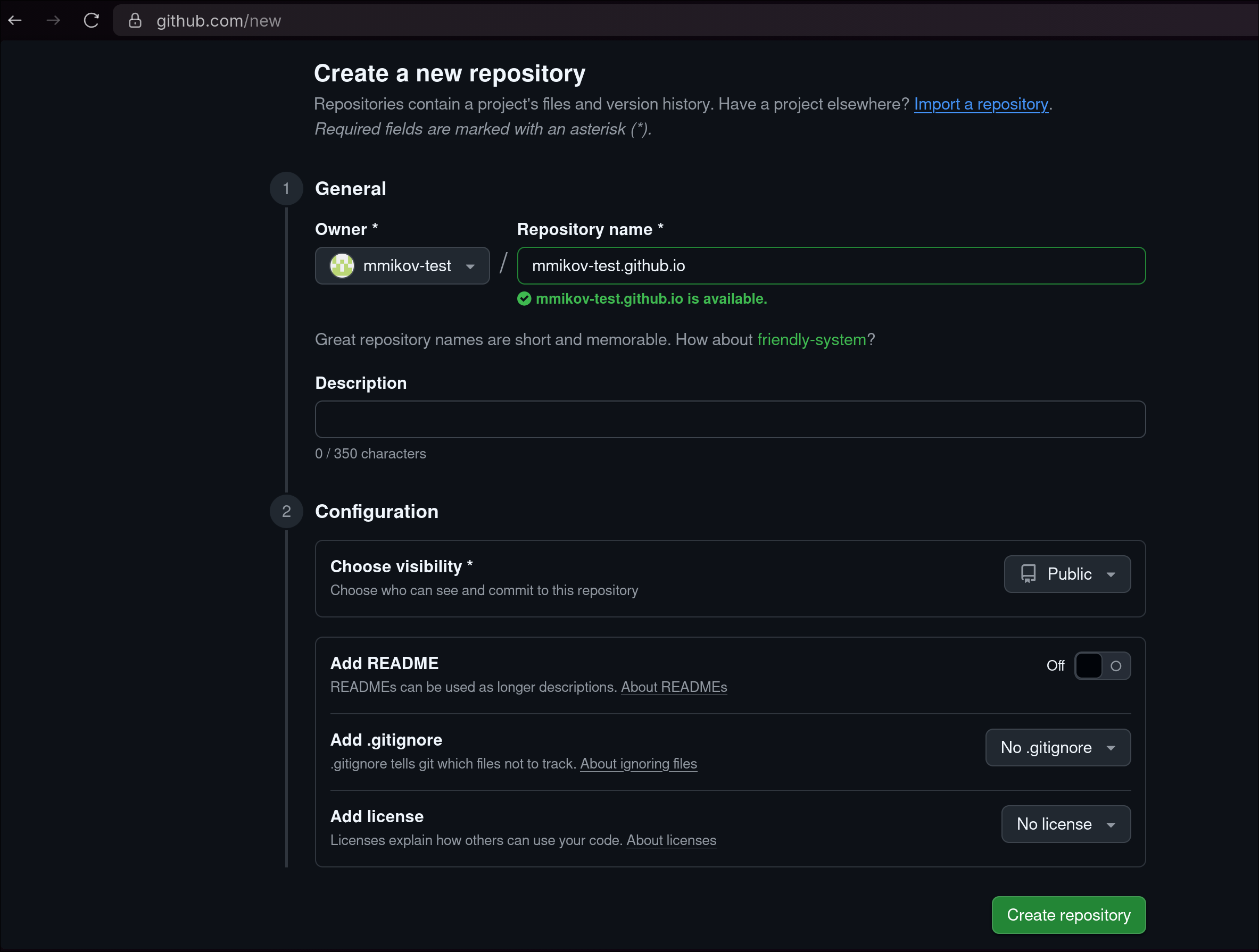
- Create a repository named
{your-handle}.github.io
Next you need to setup your local repository.
Setting up on your personal computer
On Linux, install git using your systems package manager. For example:
apt install git # for Debian / Ubuntu
pacman -Sy git # for Arch
dnf install git # for FedoraOn MacOS, use brew to install git, or download and install it through the git website
brew install gitOn Windows, install git and git bash from the git website
After installation, git bash should appear in your start menu
Git bash provides a decent way of using bash and git on Windows
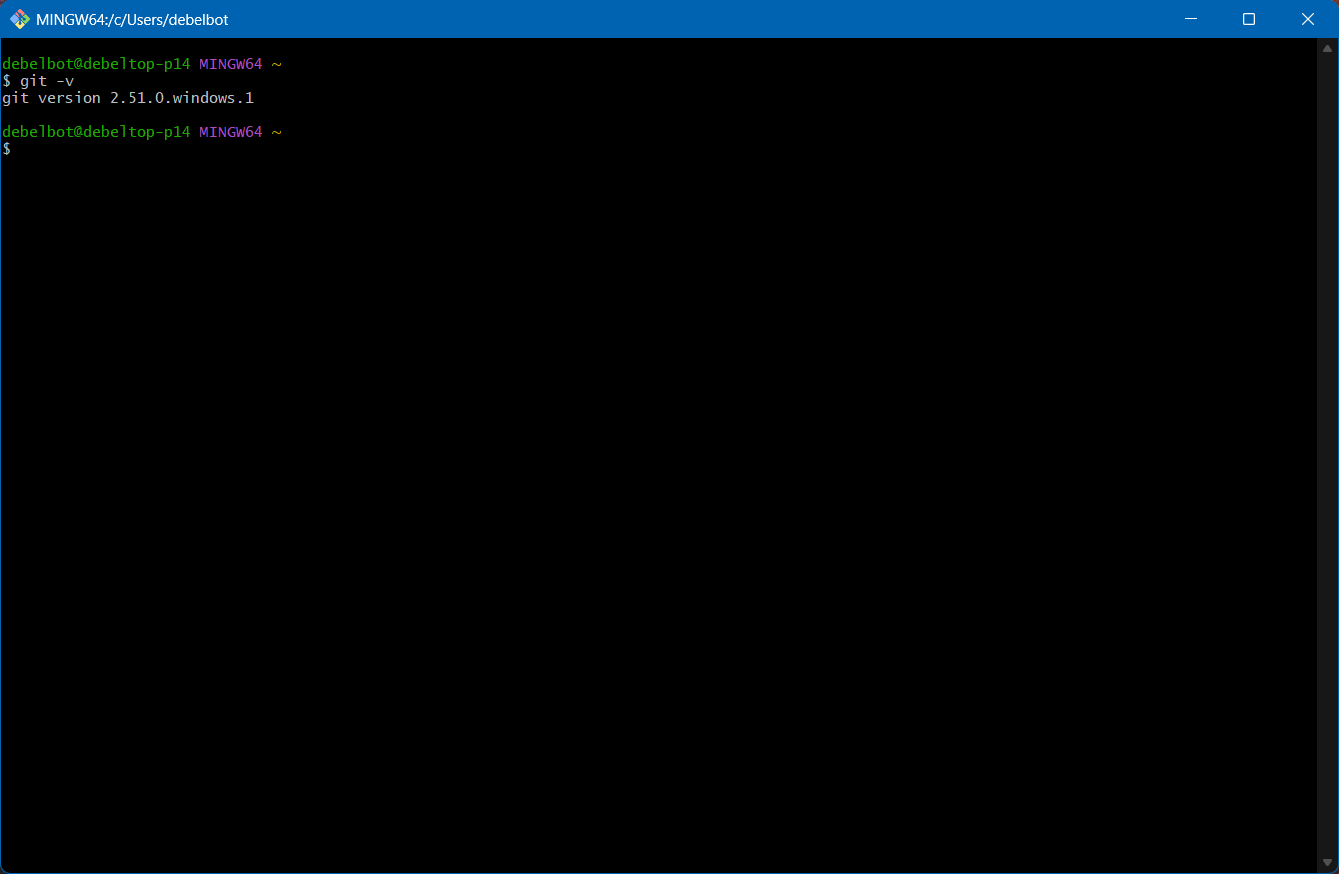
Setup a local repository
-
Use the instructions above to create an SSH key pair
-
Create a local repository, create an
index.htmlfile and commit it
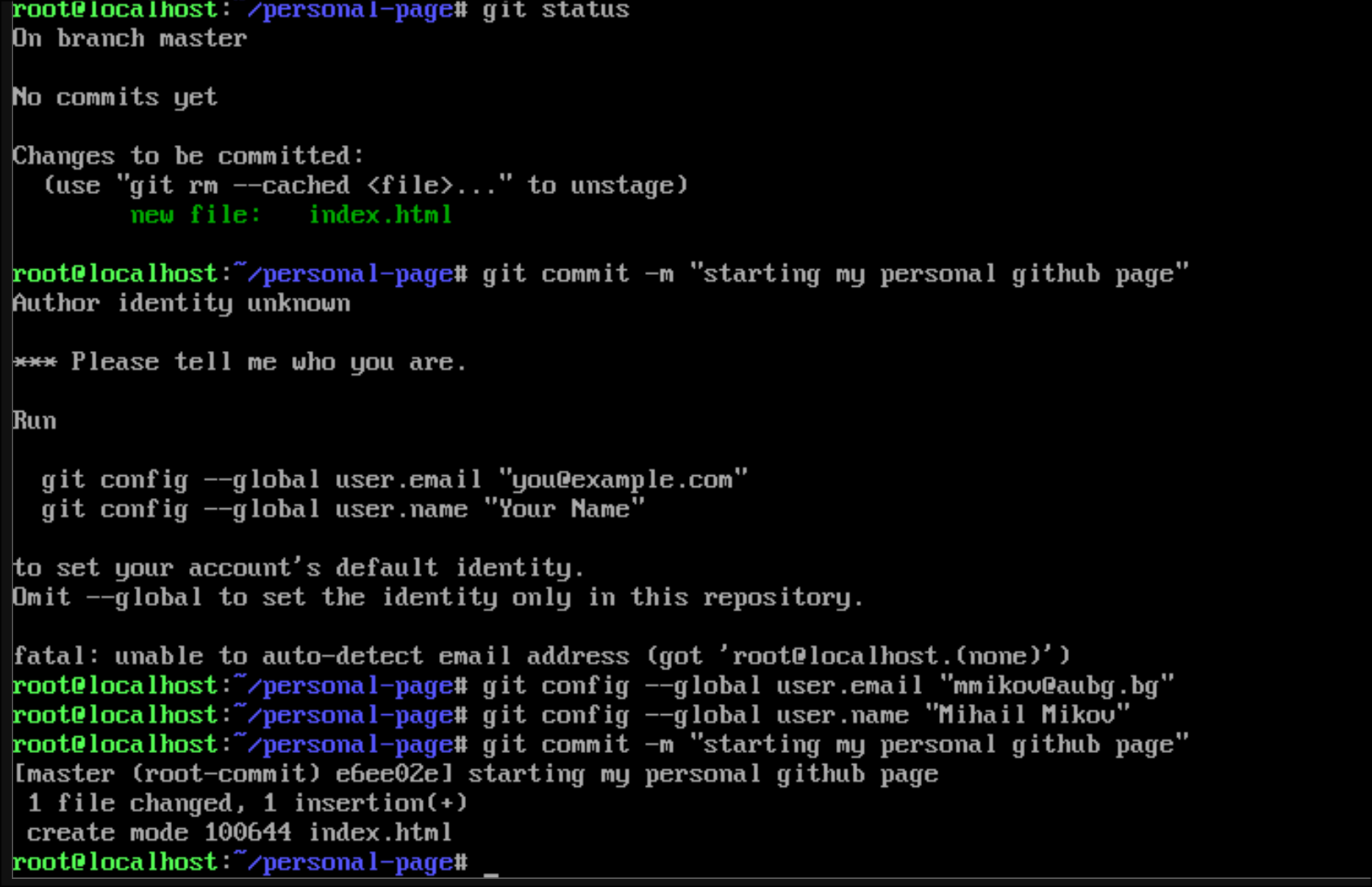
- Add the Github repository as a remote
There are 2 options:
- SSH
- HTTPS
When using HTTPS, setup the remote using the command:
git remote add github https://{your-handle}:{your-PAT}@github.com/{your-handle}/{your-handle}.github.io.gitSee HTTPS repository with PAT for more details
If you are using SSH, add the remote with this command:
git remote add github git@github.com:{your-handle}/{your-handle}.github.io.git- Push too the remote repository
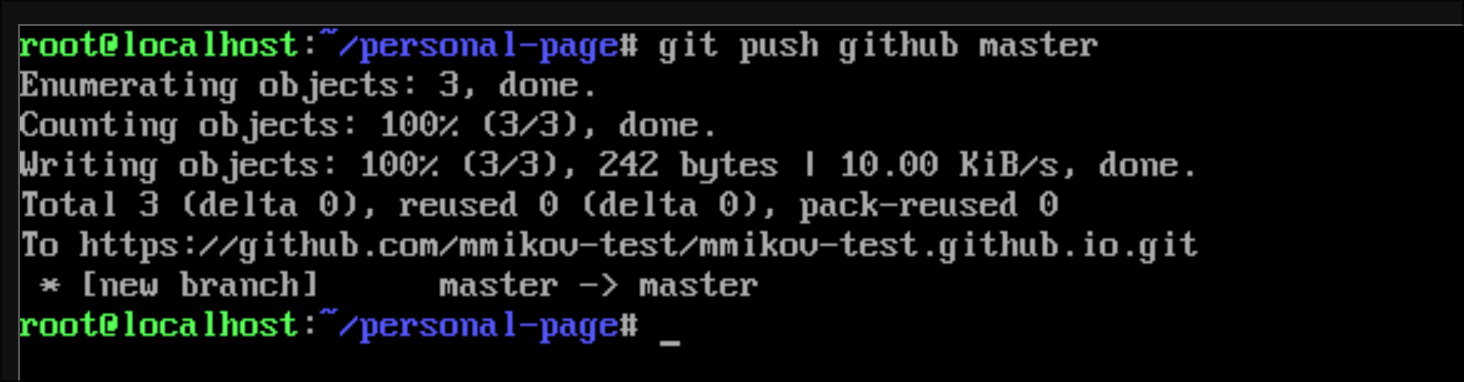
Verify the commit has been pushed on the repository page
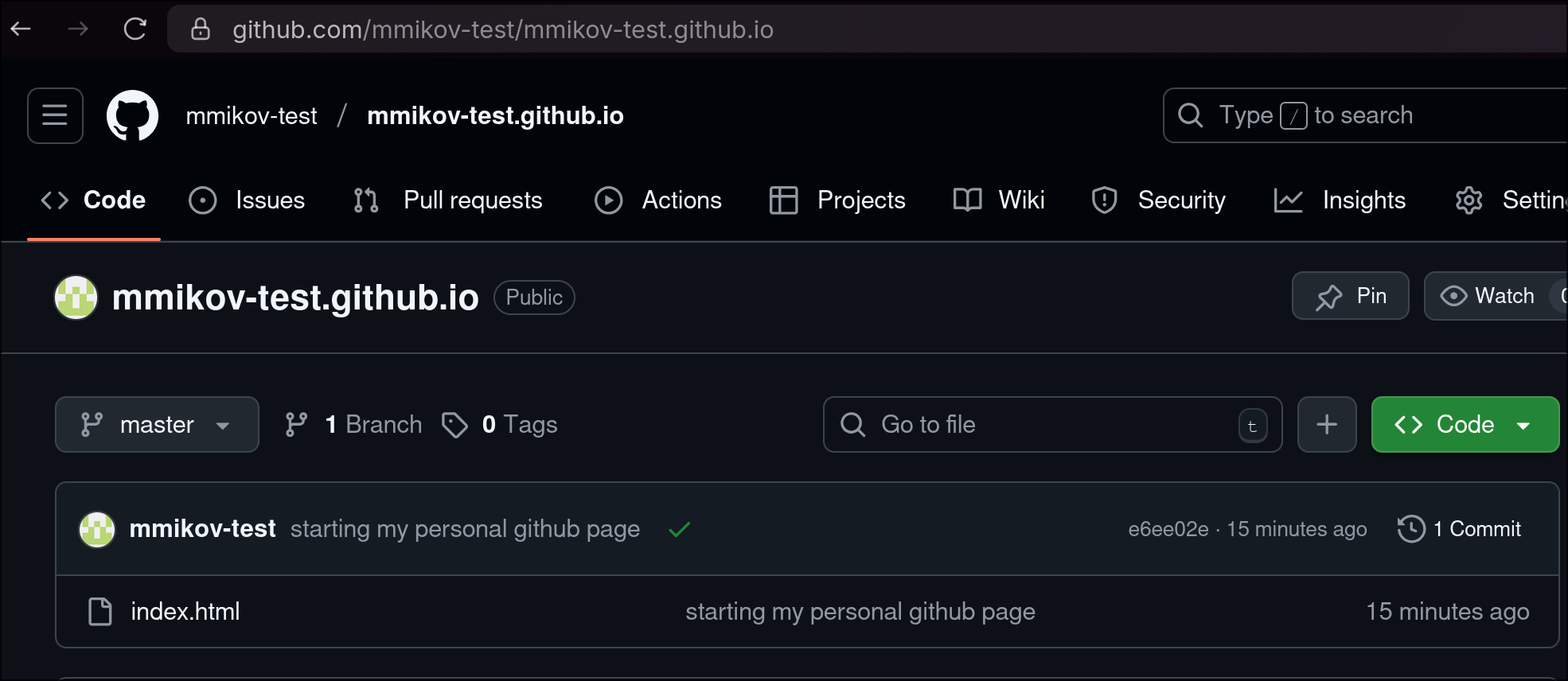
- Enable
Github Pagesin the repository’s Github settings
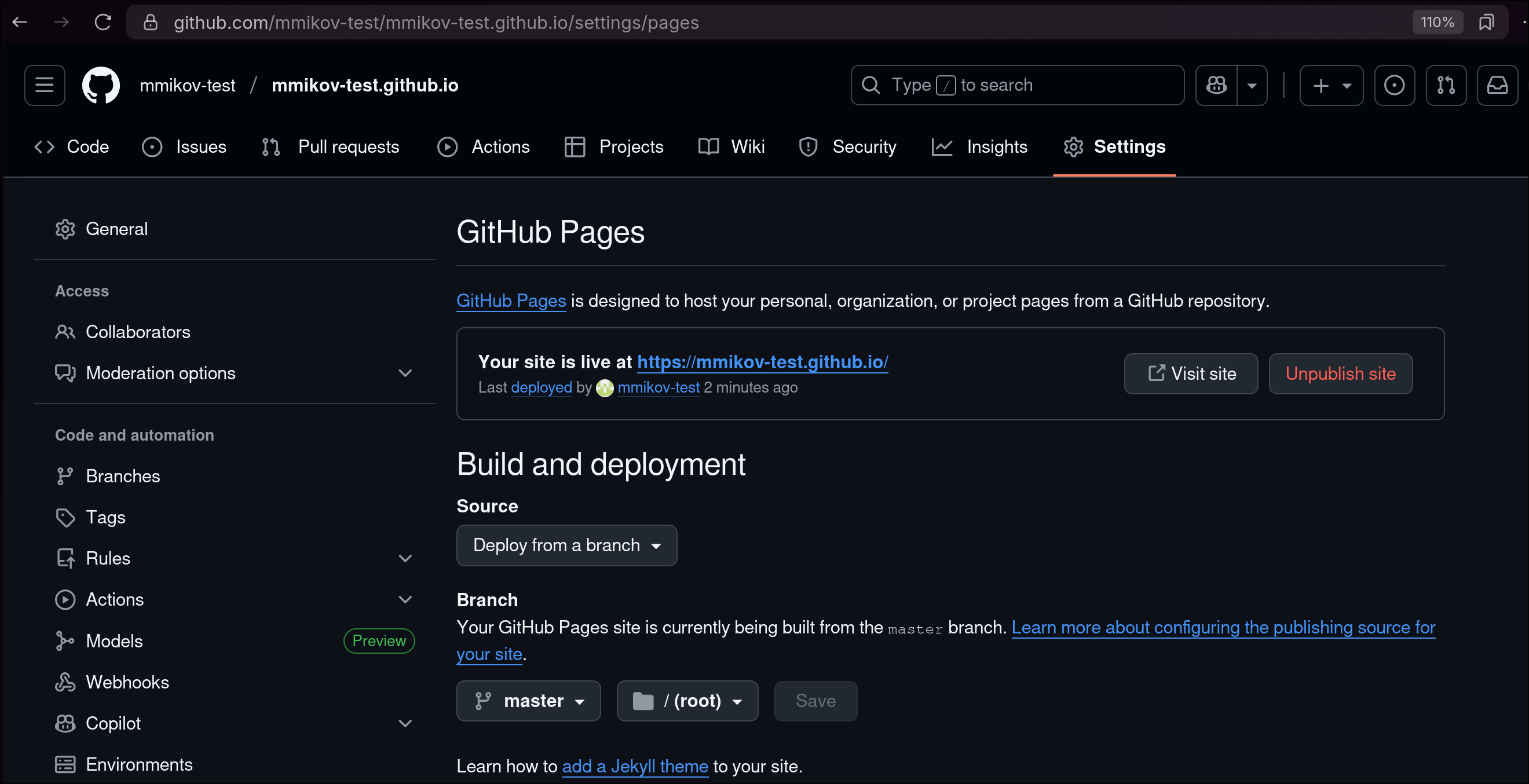 (this might be enabled by default, should look like the picture above)
(this might be enabled by default, should look like the picture above)
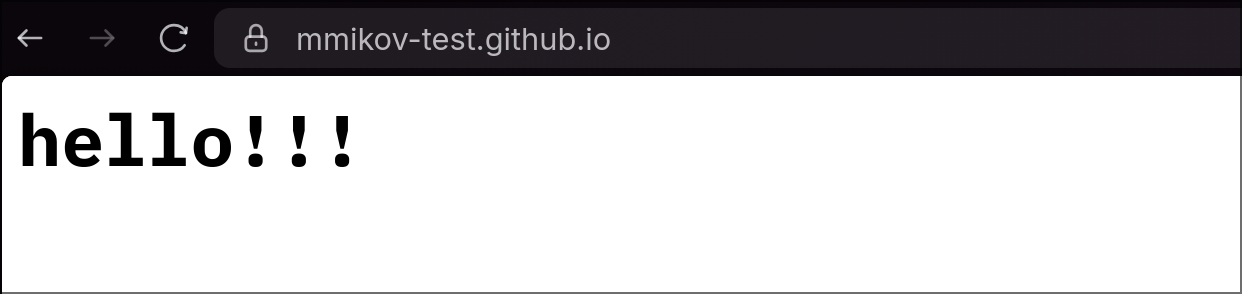
- Open your personal github site at https://{your-handle}.github.io
Specifics of using the online terminal
WARNING: The online terminal linked in this site is a good way to play around, but it is NOT suitable for daily, repeated use. Each time you refresh the page, all your files and settings WILL BE LOST.
Use it only as a last resort, if you are unable to setup your own environment.
- Enable networking
The emulated VM comes with a handy script to enable internet access from within the virtual machine:
./networking.sh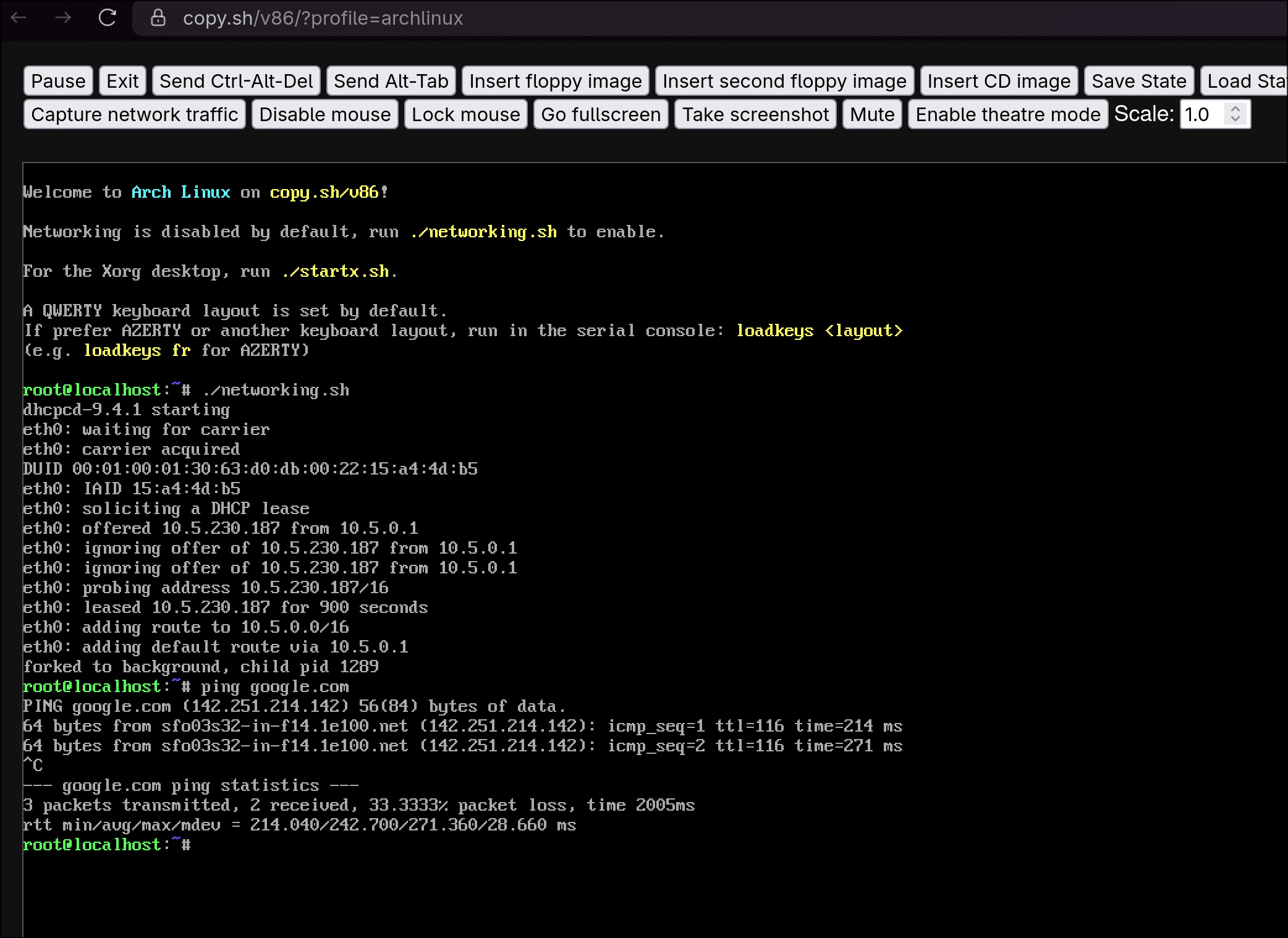
- Follow the guide for creating a local repository from above
If you create your SSH keys in the online terminal, DOWNLOAD BOTH your keys so you can reuse it later.
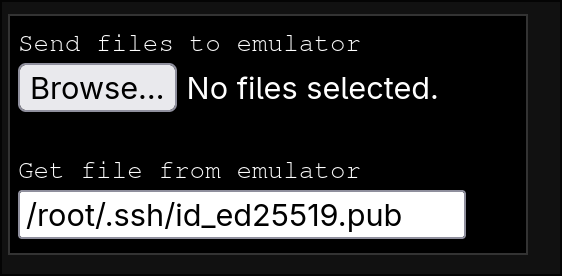
For repeated use of the online terminal
- Copy your private key to the online terminal using the upload / download widget on the page

- Clone your existing github repository
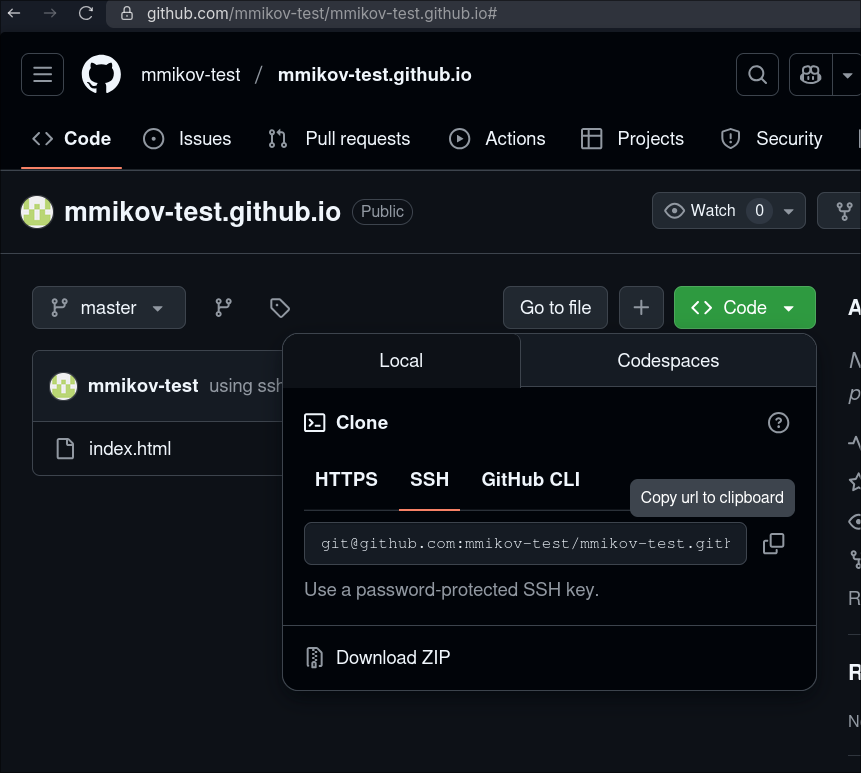
If you choose to use HTTPS, you will need to alter the URL to include authentication as shown above
- Make changes and deploy them to Github
Use git add, git commit and git push
Unfortunately, you will need to repeat this every time your refresh the online terminal.